대류 열전달 : 대만 (필즈 엔지니어링) BEDD 17 - NVLNG-ITECO-FD-SA-CAL-100_Sizing Calculation LNG Tank_Rev.3.pdf
참고1 : Vapour to Roof ( 대류 : Suspended Deck ), h = 22 W/(m²·℃)
참고2 : Roof Plate to Air ( 대류 : ), h = 68 W/(m²·℃)
참고3 : Liquid to Shell Side ( 대류 ) , h = 3500 W/(m²·℃)
참고4 : Outer Shell Plate to Air ( 대류 ), h = 68 W/(m²·℃)
참고5 : Liquid to Bottom Plate ( 대류 ) , h = 3500 W/(m²·℃)
참고6 : Under the Concrete slab to Air ( 대류 : ), h = 45 W/(m²·℃)
| No. | Insulation Material | Symbol | 보냉재 두께
t | 열전도도
k | Film Coeff.
h | R = t/k
OR
R = 1/h | Temperature
Difference
δt=△T · (R/∑R) | Face
Temperature | Remark |
| m | W /(m·℃) | W/(m²·℃) | (m²·℃) / W | ℃ | ℃ |
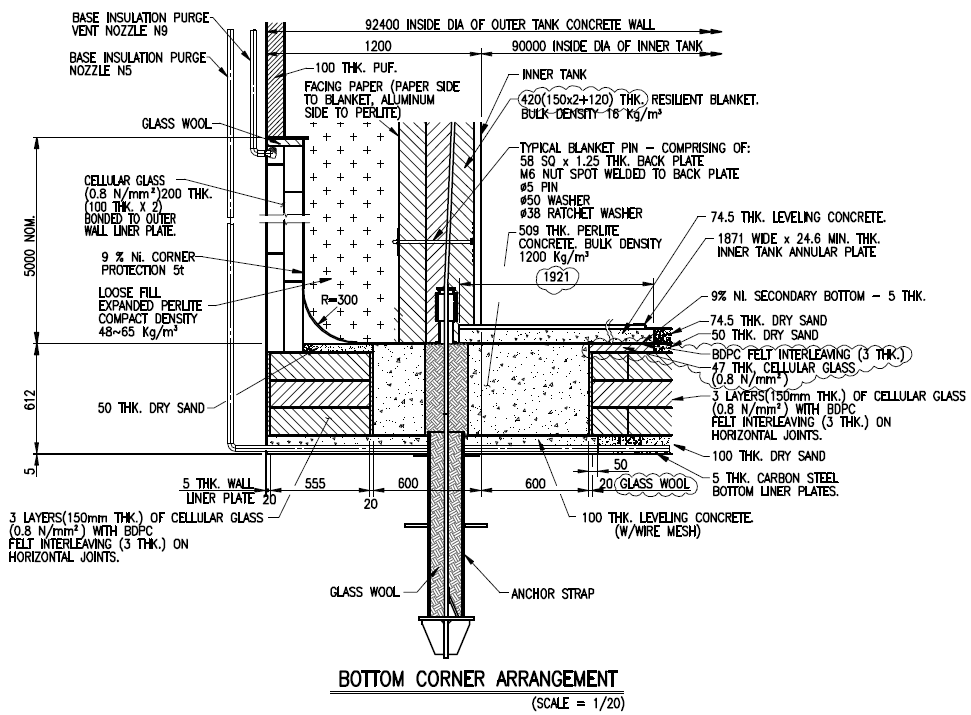
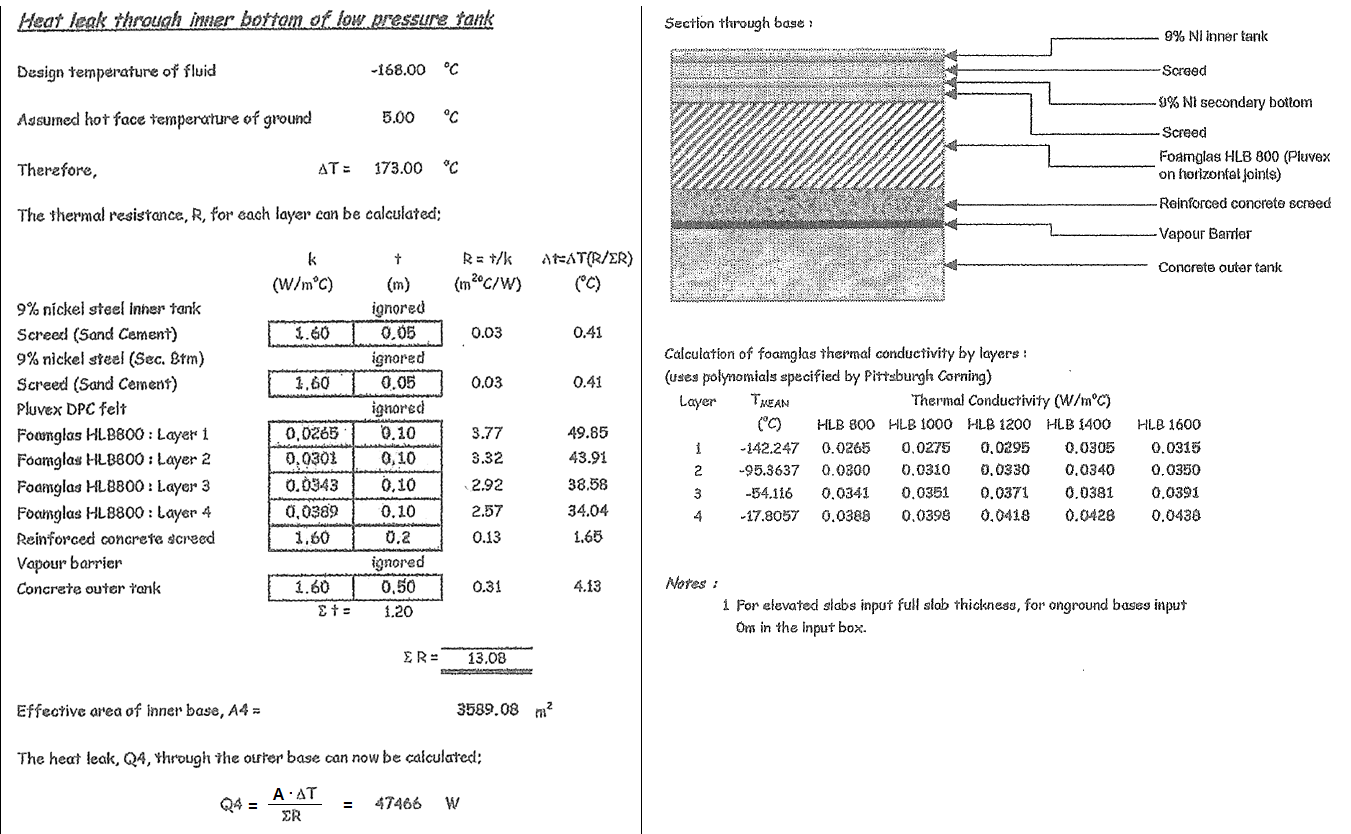
| 1 | Liquid to Bottom Shell (Convection) | | | | 3500 | 0.00029 | 0.0038 | -168.00 | |
| 2 | 9% Nickel Steel (inner tank) | ignored | 0.005 | 30.0 | | 0.00017 | 0.0022 | -167.99 | |
| 3 | Screed ( Sand Cement ) | | 0.050 | 1.6 | | 0.03125 | 0.4125 | -167.58 | |
| 4 | 9% Nickel Steel (2nd Bottom) | ignored | 0.005 | 30.0 | | 0.00017 | 0.0022 | -167.58 | |
| 5 | Screed ( Sand Cement ) | | 0.050 | 1.6 | | 0.03125 | 0.4125 | -167.17 | |
| 6 | BDPC Felt (Pluvex DPC Felt) | ignored | | | | 0.00000 | 0.0000 | 0.00 | |
| 7 | Form Glass HLB 800 : Layer 1 | at -142.247 ℃ | 0.100 | 0.0265 | | 3.77358 | 49.8150 | -117.35 | |
| 8 | Form Glass HLB 800 : Layer 2 | at -95.3637 ℃ | 0.100 | 0.0301 | | 3.32226 | 43.8571 | -73.49 | |
| 9 | Form Glass HLB 800 : Layer 3 | at -54.116 ℃ | 0.100 | 0.0343 | | 2.91545 | 38.4868 | -35.01 | |
| 10 | Form Glass HLB 800 : Layer 4 | at -17.8057 ℃ | 0.100 | 0.0389 | | 2.57069 | 33.9357 | -1.07 | |
| 11 | Reinforced Concrete Screed | | 0.200 | 1.6 | | 0.12500 | 1.6501 | 0.58 | |
| 12 | Vapour Barrier ( 3rd Btm Steel ? ) | ignored | 0.005 | 20.0 | | 0.00025 | 0.0033 | 0.58 | |
| 13 | Concrete Outer Tank | | 0.500 | 1.6 | | 0.31250 | 4.1253 | 4.71 | |
| 14 | Air to Concrete (Convection) | ignored | | | 45 | 0.02222 | 0.2934 | 5.00 | |
| Total Wall Thickness, Thk = ∑t | Thk = | 1.215 | | | | | | |
| Total Thermal Resistance Ratio, ∑R
(전체 열저항율) | | | | ∑R = | 13.105 | (m²·℃) / W | | |
| BOG Calculation Result : |
| No. | Description | SI Unit | Metric | | |
| 1 | Contents(LNG) Temperature | Ti = | -168 | ℃ | Ti = | 105.15 | K | | |
| 1 | Outer Surface Temperature | To = | 5 | ℃ | To = | 278.15 | K | | |
| 1 | Temperature difference △T =To-Ti | △T = | 173 | ℃ | △T = | 173 | K | | |
| 2 | Effective Insulation Area | A = | 3589.08 | m² | A = | 3589.08 | m² | | |
| 3 | Overall heat transfer coefficient, U = 1 / ∑R | U = | 0.07631 | W / (m²·℃) | U = | 0.06561 | kcal / (m²·K) | | |
| 4 | Total Heat Leak(방산열량) Q = U·△T·A | Q = | 47379.4 | W | Q = | 40766.2 | kcal / hr | | |
| 5 | Heat Flex(열유속) q = △T / ∑R or Q / A | q = | 13.201 | W / m² | q = | 11.3508 | kcal / (hr·m²) | | |
| 9 | Latent heat of vaporization of LNG(증발잠열) by P.O.S | h = | 511000 | J / kg | L = | 122.05 | kcal / kg | | |
| 10 | [Design Data] Net Storage Capacity (90%) | V = | 475.35 | m³ | V = | 475.35 | m³ | | |
| 11 | Density of LNG (by P.O.S) | ρ = | 425 | kg / m³ | ρ = | 425 | kg / m³ | | |
| 12 | Content Weight of LNG (총질량), F = V ⋅ ρ | F = | 202024 | kg | F = | 202024 | kg | | |
| 29 | Heat Leak Weight per one hour
(시간당 열손실중량), Wt = 3600 ⋅ Q / h | Wt = | 333.7883 | kg / hr | Wt = | 333.7883 | kg / hr | | |
| 13 | (POS) Boil Off Rate per Day | BOR(POS)= | 0.3 | %/day | | | | | |
| 14 | (Calculate) Boil Off Rate per Day
BOR(day) = 24⋅3600⋅100 ⋅ Q / (h ⋅ F) | BOR(day)= | 3.9653 | %/day | | | | | |
| 15 | Check, Calcute BOR(day) < BOR(design) | | NG! | | | | | | |
| 40 | Leakage Weight per Day, W_loss = F ⋅ BOR / 100 | W_loss = | 8010.92 | kg/day | | | | | |
| 41 | Leakage Volume per Day, V_loss = W_loss / ρ | V_loss= | 18.8492 | m³/ kg | | | | | |
| 16 | Days of Vaporization of Liquid(Evaporation)
, Hdays = F / W_loss | Hdays = | 25.22 | day | | | | | |
Where ,Insulation System of PUF SPRAY type applicable to LPG/LEG/LNG liquidified cargi tank