| Description | Symbol | Value | Unit | Description |
| Stress due to internal pressure, Sp = P⋅R / (2⋅ts) | Sp = | 63.952 | MPa | Sp = P⋅R / (2⋅ts) |
| Stress due to external pressure, Spe = Pe⋅R / (2⋅ts) | Spe = | 5.1923 | MPa | Spe = Pe⋅R / (2⋅ts) |
M1 = Bending Moment at saddles
 = 2.91340722E8 N-mm = 2.91340722E8 N-mm | M1 = | 291 | KN-m | |
M2 = Bending Moment at shell midspan
 = 2.736292469E9 N-mm = 2.736292469E9 N-mm | M2 = | 2736 | KN-m | |
| [ S1.a ] Longitudinal stress at saddle support - Without Stiffeners [내부 RING 보강 안됨] |
| Bending Moment of Saddle location | M1 = | 291340722 | N-mm | at saddle support |
| Coefficients K1 | K1 = | 0.718 | | A/R = 0.28 [TABLE 1] |
| Coefficients K8 | K8 = | 1.183 | | A/R = 0.28 [TABLE 1] |
| Longitudinal stress at Saddle(+ 인장), S1.a = (±)M1 / (K1 ⋅ R²⋅ t) | S1.a = | 3.4681 | MPa | S1.a = M1 / (K1 ⋅ R²⋅ t) |
| Longitudinal stress at Saddle(- 압축), S1.a = (-)M1 / (K8 ⋅ R²⋅ t) | S1.a = | -2.1049 | MPa | S1.a = M1 / (K8 ⋅ R²⋅ t) |
| Maximum tensile stress, (+ 인장), S1t.a = S1.a + Sp | S1t.a = | 67.4201 | MPa | < St (213.3 MPa) OK |
| Maximum compressive stress (- 압축), S1c.a = -S1.a - Spe | S1c.a = | -3.0874 | MPa | < Sc (59.47 MPa) OK |
| Tensile stress is acceptable ( S1t.a < St = 213.3 MPa ) | St = | 213.3 | MPa | St = S ⋅ E |
| Compressive Stress is acceptable ( S1c.a < Sc = 59.47 MPa ) | Sc = | 59.47 | MPa | Sc =Et/29 ⋅ (ts/R)⋅[2-(2/3)⋅100⋅(ts/R)] |
| [ S1.a ] Longitudinal stress at saddle support - With Stiffeners [내부 RING 보강 된 경우] |
| Bending Moment of Saddle location | M1 = | 291340722 | N-mm | at saddle support |
| M11 = 6⋅Q/12⋅[(8⋅A⋅H + 6⋅A² - 3⋅R² + 3⋅H²) / (3⋅L+4⋅H)] | M11 = | 291340722 | N-mm | at saddle support |
| Stress due to internal pressure, Sp = P⋅R / (2⋅ts) | Sp = | 63.95 | MPa | Sp = P⋅R / (2⋅ts) |
| Longitudinal stress at Saddle(+ 인장), S1t = (+)M1 / (π ⋅ R²⋅ t) | S1t = | (+) 0.7926 | MPa | S1t = +M1 / (π ⋅ R²⋅ t) |
| Longitudinal stress at Saddle(- 압축), S1c = (-)M1 / (π ⋅ R²⋅ t) | S1c = | (-) 0.7926 | MPa | S1c = -M1 / (π ⋅ R²⋅ t) |
| Maximum tensile stress, (+ 인장), S1t.a = S1t + Sp | S1t.a = | (+) 64.7447 | MPa | < St (213.3 MPa) OK |
| Maximum compressive stress (- 압축), S1c.a = -S1c | S1c.a = | (-) 0.7926 | MPa | < Sc (59.47 MPa) OK |
| [ S1.b ] Longitudinal stress at shell midspan |
| Bending Moment of Shell mid-point | M2 = | 2736292469 | N-mm | at shell center, Shell 중간지점 |
| M22 = 3⋅Q/12⋅[(3⋅L²+6⋅R²-6⋅H²-12⋅A⋅L-16⋅A⋅H) / (3⋅L+4⋅H)] | M22 = | 2736292469 | N-mm | at shell center, Shell 중간지점 |
| Longitudinal Stress at Shell Ceneter, S1.b = M2 / (π ⋅ R²⋅ t) | S1.b = | 7.4443 | MPa | S1.b = M2 / (π ⋅ R²⋅ t) |
| Maximum tensile stress, S1t.b = S1.b + Sp | S1t.b = | 71.3964 | MPa | < St (213.3 MPa) OK |
| Maximum compressive stress (shut down), S1c.b = -S1.b - Spe | S1c.b = | -12.6367 | MPa | < Sc (59.47 MPa) OK |
| Tensile stress is acceptable ( S1t.b < St = 213.3 MPa ) | St = | 213.3 | MPa | St = S ⋅ E |
| Compressive Stress is acceptable ( S1c.b < Sc = 59.47 MPa ) | Sc = | 59.4713 | MPa | Sc =Et/29 ⋅ (ts/R)⋅[2-(2/3)⋅100⋅(ts/R)] |
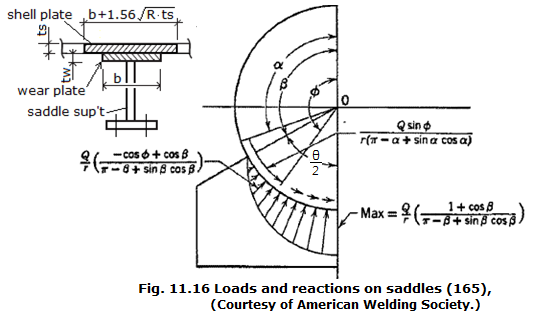
| [ S2.a ] [접선 전단] Tangentinal shear stress on shell (S2) A = 840.0(mm) > R/2=1500.0 (mm) |
| Coefficients K2 | K2 = | 0.577 | | [TABLE 1] |
| at Shell [CASE a] A > R/2, S2a = K2⋅Q/R⋅ts ⋅ (L-2A/L+4/3H) | S2a = | 14.5622 | MPa | < 0.8·S (171 MPa) OK |
| at Shell [CASE b] A > R/2, S2b = K3⋅Q/R⋅ts ⋅ (L-2A/L+4/3H) | S2b = | 8.0256 | MPa | < 0.8·S (171 MPa) OK |
| [ S2.b ] [접선 전단] Tangentinal shear stress on shell (S2) A = 840.0(mm) ≤ R/2=1500.0 (mm) |
| Coefficients K4 | K4 = | 0.26 | | [TABLE 1] |
| Coefficients K5 | K5 = | 0.216 | | [TABLE 1] |
| at Shell [CASE d] A ≤ R/2, S2d = K4⋅Q / (R⋅ts) | S2d = | 8.9241 | MPa | < 0.8·S (171 MPa) OK |
| at Head [CASE e] A ≤ R/2, S2e = K4⋅Q / (R⋅th) | S2e = | 12.8903 | MPa | < 0.8·S (171 MPa) OK |
| at Addtional Stress at Head [CASE f] A ≤ R/2, S3 = K5⋅Q / (R⋅th) | S3 = | 10.7089 | MPa | < 1.25·S (267 MPa) OK |
| [ S4 ] Circumferential Bending Stress at the horn of saddle - shell not Stiffened [원주상 보강안됨, 원뿔부위] (S4) |
| Coefficients K2 | K6 = | 0.018 | | For Saddle contact angle θ=180.0 deg.[TABLE 1] |
at Saddle Horn [CASE a] L ≥ 8R [보강안됨, 원뿔부위]
S4a= -Q / [4⋅ts⋅( b+1.56⋅Sqrt(R⋅ts)] - [ 3⋅K6⋅Q / (2⋅ts²)] | S4a = | -233.54 | MPa | < 1.5·S (320 MPa) OK |
at Saddle Horn [CASE b] L < 8R [보강안됨, 원뿔부위]
S4b= -Q / [4⋅ts⋅( b+1.56⋅Sqrt(R⋅ts)) - [ 12⋅K6⋅Q / (2⋅ts²)] | S4b = | -369.32 | MPa | < 1.5·S (320 MPa) NG! 내부 RING 보강 필요 |
| [ S5.a ] Circumferential compression Stress at bottom of Shell (S5.a : Wear Plate 가 없다고 가정하고 계산 한 것.) |
| Shell plate thickness | ts = | 13 | mm | |
| Wear plate thickness | tw = | 22 | mm | |
| Saddle Width | b = | 1000 | mm | |
| Coefficients K7 = | K7 = | 0.654 | | |
a) when, No Wear Plate S5 = Wear Plate 가 없다고 가정하고 계산 한 것.
Note: ts = ts + tw only if wear plate is attached to shell and width
of wear plate is a min. of b+1.56⋅Sqrt((R⋅ts)) Width of wear plate
S5a = -K7 ⋅ Q / [ts ⋅ (b+1.56⋅Sqrt(R⋅ts))] | S5a = | -51.45 | MPa | < 0.5Sy (225 MPa) OK |
| [ S5.b ] Stress at bottom of Shell, Wear plate-Ring compression in shell over saddle (S5.b : Wear Plate가 있을 경우) |
| Attached angle of wear plate | α = | 95 | degree | |
| Combind Thickness of shell wear plate thickness | tw = | 22 | mm | |
| Width of wear plate, | bWear = | 862 | mm | |
| Effective Section Area Aeff = ts⋅ [b+1.56⋅Sqrt(R⋅ts)]+ tw⋅bWear | Aeff = | 45556 | mm² | |
 | |
| Coefficients K7 = | K7 = | 0.654 | | |
| b) Stress at bottom of Shell, Wear plate-Ring compression, S5b = -K7⋅Q / Aeff | S5b = | -19.2 | MPa | < 0.5Sy (225 MPa) OK |
| [ S6 ] Inner Ring Stiffener Stress at the saddle (S6), when Ring Stiffener Attached shell inside |
| Coefficients K9, K10 refer to P/V HANDBOOK page 95 Table. | | | | |
| Coefficients K9 when, θ = 160 degree. | K9 = | 0.25 | | |
| Coefficients K10 when, θ = 160 degree. | K10 = | 0.017 | | |
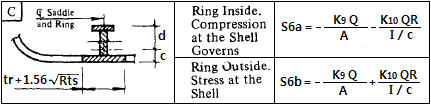 | Acomb = | 52927 | mm² | Acomb= 318.0 cm2 |
| C = | 509.5 | mm | C1 = 56.32 mm, C2= 44.98 mm, b=32.31 mm |
| R = | 3000 | mm | |
| Icomb = | 8192000000 | mm⁴ | Ix= 448904.52 cm⁴ |
a) Ring Inside. Compression at the Shell Governs
S6a = -(K9⋅Q / A) - [(K10⋅Q⋅R⋅C) / I] | S6a = | -10.57 | MPa | < 1.0·S (213 MPa) OK |
b) Ring Outside Stress at the Shell
S6b = -(K9⋅Q / A) + [(K10⋅Q⋅R⋅C) / I] | S6b = | -2.08 | MPa | < 0.5·S (225 MPa) OK |
| 0 | M1 = Bending Moment at saddles
 = 2.91340722E8 N-mm, = 2.91340722E8 N-mm, | M1 = | 2.91340722E8 | N-mm, M1 = 291 KN-m |
| 1 | M2 = Bending Moment at shell midspan
 = 2.736292469E9 N-mm, = 2.736292469E9 N-mm, | M2 = | 2.736292469E9 | N-mm, M2 = 2736 KN-m |
| 2 | Sp = Stress due to internal pressure
Sp = P⋅R / 2⋅ts | Sp = | 63.95 | MPa |
| 3 | S1 = Longitudinal bending at saddles - without stiffeners, tension (+인장)
S1a = (+) M1 / (K1 ⋅ R² ⋅ ts) | S1a = | (+) 3.47 | MPa |
| 4 | S2 = Longitudinal bending at saddles - without stiffeners, compression (-압축)
S1b = (-) M1 / (K8 ⋅ R² ⋅ ts) | S1b = | (-) 2.1 | MPa |
| 5 | S3 = Longitudinal bending at saddles - with stiffeners (+인장, -압축)
S1c = (±) M1 / (π ⋅ R² ⋅ ts) | S1c = | ( ± ) 0.79 | MPa |
| 6 | S4 = Longitudinal bending at shell midspan, tension at bottom, compression at top (+인장, -압축)
S1d = (±) M2 / (π ⋅ R² ⋅ ts) | S1d = | ( ± ) 7.44 | MPa |
| 7 | S5 = Tangential shear - shell stiffened in plane of saddle (내부 RING 에 의하여 보강됨)
S5 = S2b = K3⋅Q/(π⋅R⋅ts) ⋅ [L-2A / L+4/3H] | S5=S2b= | 8.03 | MPa |
| 8 | S6 = Tangential shear - shell not stiffened, A > R/2 (보강안됨)
S6 = S2a = K2⋅Q/(R⋅ts) ⋅ [L-2A / L+4/3H] | S6=S2a = | 14.56 | MPa |
| 9 | S7 = Tangential shear - shell not stiffened except by heads, A ≤ R/2 (보강안됨)
S7 = S2d = K4⋅Q/(R⋅ts) | S7=S2d = | 8.92 | MPa |
| 10 | S8 = Tangential shear in head - shell not stiffened, A ≤ R/2 (보강안됨)
S8 = S2e = K4⋅Q/(R⋅th) | S8=S2e = | 12.89 | MPa |
| 11 | S8a = Tangential shear in head , ( Addtional Stress ), A ≤ R/2 (보강안됨)
S8a = S3 = K5⋅Q/(R⋅th) | S8a=S3 = | 10.71 | MPa |
| 12 | S8b = Tangential shear in head , 보강됨 OR A > R/2 = S8 = 0 MPa
S8b = 0.0 | S8b = | 0.0 | MPa |
| 13 | S9 = Circumferential bending at horn of saddle - shell not stiffened, L ≥ 8R
S9=S4a= -Q / [4⋅ts⋅( b+1.56⋅Sqrt(R⋅ts)] - [ 3⋅K6⋅Q / (2⋅ts²)] | S9=S4a= | -233.54 | MPa |
| 14 | S10 = Circumferential bending at horn of saddle - shell not stiffened, L < 8R
S10=S4b= -Q / [4⋅ts⋅( b+1.56⋅Sqrt(R⋅ts)) - [ 12⋅K6⋅Q / (2⋅ts²)] | S10=S4b= | -369.32 | MPa |
| 15 | S11 = Additional tension stress in head - shell not stiffened, A ≤ R/2
S11 = S3 = K5⋅Q/(R⋅th) | S11=S3 = | 10.71 | MPa |
| 16 | S12 = Circumferential compressive stress - stiffened or not stiffened, saddles attached or not)
S12=S5a = -K7 ⋅ Q / (ts ⋅ [b+1.56⋅Sqrt(R⋅ts)] | S12=S5a = | -51.45 | MPa |
| 17 | S13 = Circumferential stress in shell with stiffener in plane of saddle
S13=S6a = -(K9⋅Q / Acomb) - [(K10⋅Q⋅R⋅c) / Icomb] | S13=S6a = | -10.57 | MPa |
| 18 | S14 = Circumferential stress in ring stiffener
S14=S6b = -(K9⋅Q / Acomb) + [(K10⋅Q⋅R⋅c) / Icomb] | S14=S6b = | -2.08 | MPa |
| Design Parameters | Symbol | Value | Unit | | |
| Design Temperature | T = | 220 | °C | | |
| Claculated Design Pressure | P = | 1.471 | MPa | 15 | kg/cm²g |
| Inside Shell Diameter | D = | 4235 | mm | | |
| Corosion Allowance | C = | 3.2 | mm | | |
| Corroded Inside Shell Diameter = (D + (2*C)) | Dc = | 4241.4 | mm | | |
| Corroded Inside Shell Radius | R = | 2120.7 | mm | | |
| Corroded Shell thicknes | ts = | 3.2 | mm | | |
| Mean radius = (R + (ts/2))) | Rm = | 2122.3 | mm | | |
| Shell length (TL to TL) | L = | 13253 | mm | | |
| Head thickness | th = | 28 | mm | | |
| Thickness of wear plate | tr = | 18 | mm | | |
| Inside Depth of head in corroded condition | H = | 1060.35 | mm | | |
| Operating weight of the vessel | Wo = | 2450377.8 | N | 249869 | kg |
| Distance from Tangent line of vesel to Center of saddle | A = | 800 | mm | | |
| Distance from center line of vessel to bottom | B = | 2200 | mm | | |
| Number of saddle | n = | 2 | Nos. | | |
| Center of Saddle to saddel distance | Ls = | 8953 | mm | | |
| Length of base plate | E = | 4370 | mm | | |
| saddle width | b = | 395 | mm | | |
| Wear Plate width | b1 = | 1200 | mm | | |
| Joint Efficiency in shell | E = | 0.85 | | | |
Allowable stress value for shell material
[As Per ASME Section - II, Part - D, Subpart 1, Table 1A]
| S = | 137.88 | MPa | | 1406 kg/cm² |
Allowable stress value for head material
[As Per ASME Section - II, Part - D, Subpart 1, Table 1A]
| S = | 137.88 | MPa | | 1406 kg/cm² |
Sr Allowable stress value for R.F Pad (wear plate) Material
[As Per ASME Section - II, Part - D, Subpart 1, Table 1A]
| Sr = | 137.88 | MPa | | 1406 kg/cm² |
Minimum Yield stress value for shell
[As Per ASME Section - II, Part - D, Subpart 1, Table - Y1]
| Sy = | 260 | MPa | | 2651.272 kg/cm² |